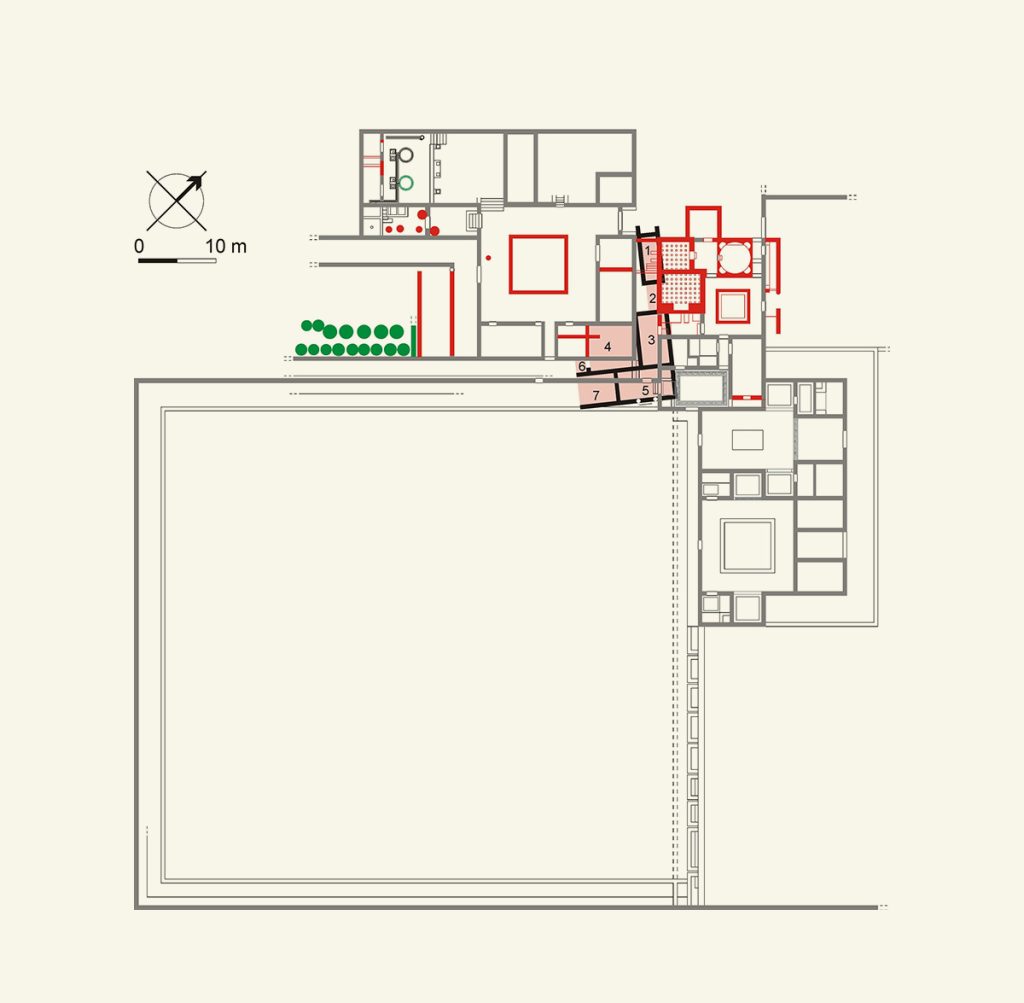
The courts
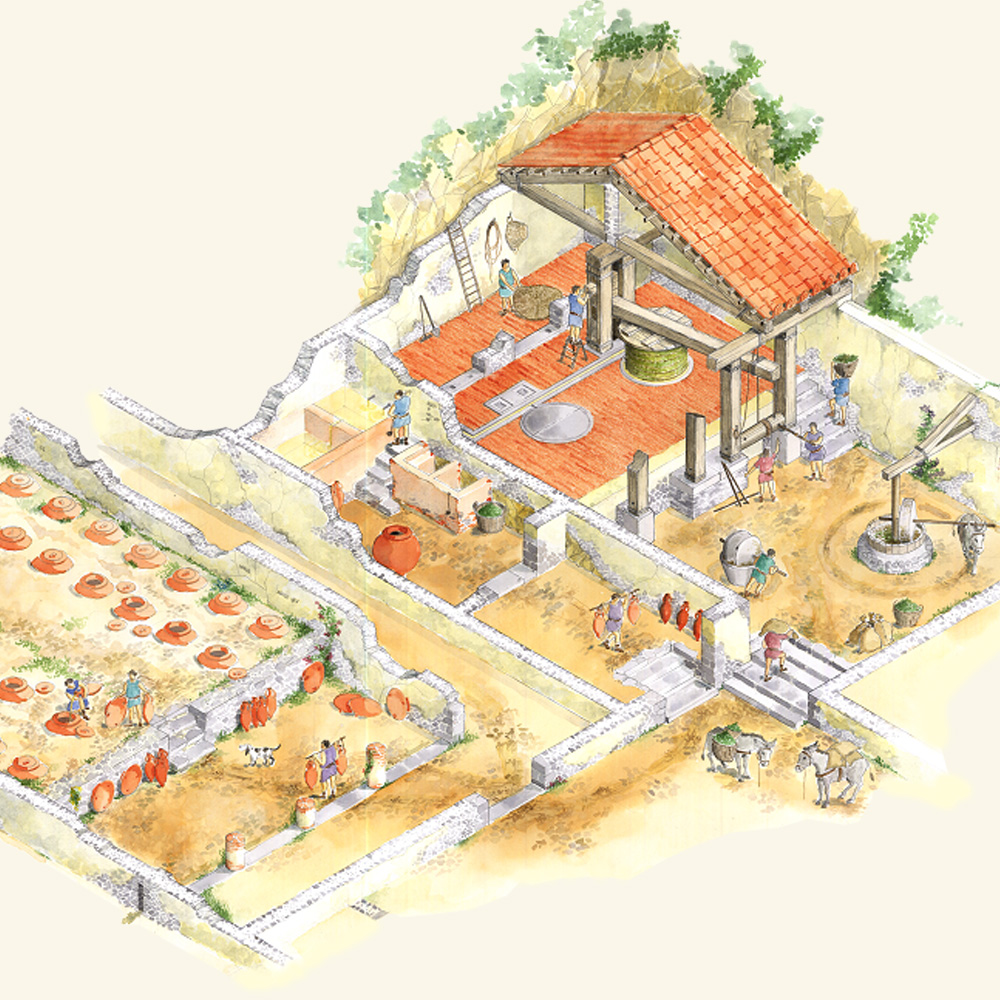
In addition to the spaces corresponding to the owner’s home and the oil mill, the Villa also included surfaces free from buildings such as the so-called “large courtyard”, a large quadrangular area, cultivated, delimited by terrace walls and the “small courtyard”, paved, around which various rooms related to agricultural activities are arranged.
The plot was completed by land intended for crops – in particular olives – and grazing.
In the archaeological excavations carried out beneath the rooms of the small courtyard, the remains of a construction from the 2nd century BC came to light, razed to the level of the cocciopesto floors, with a different orientation from that of the system that overlaps it.
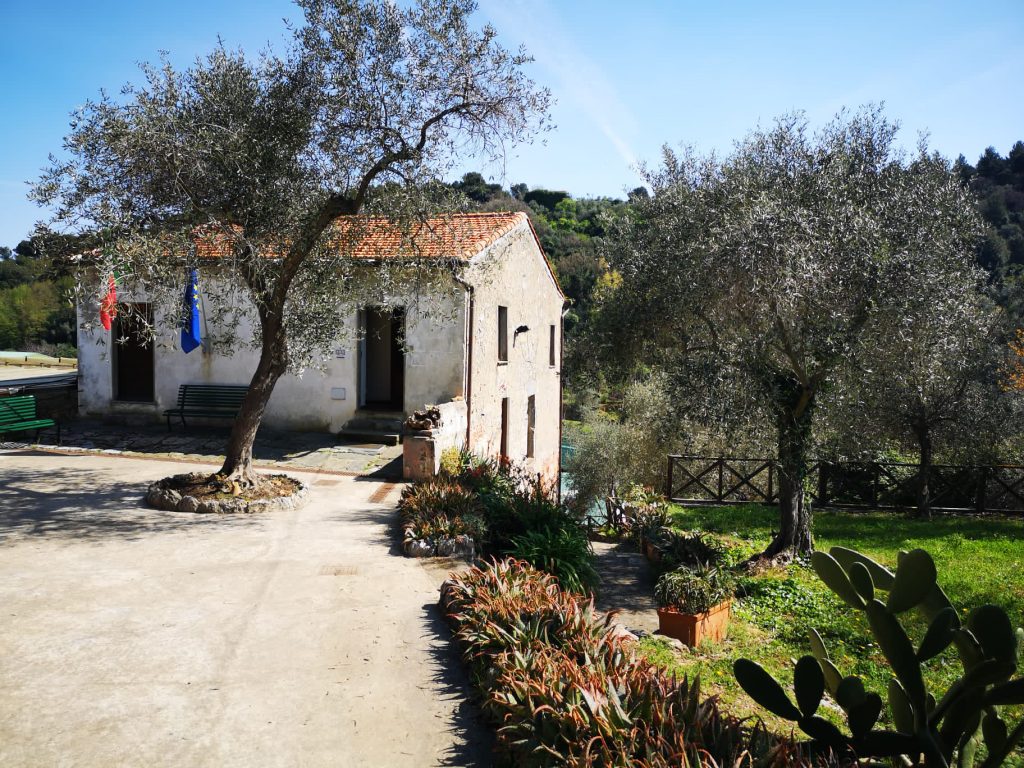
In the strip between the two courtyards was positioned the oil cellar for storing oil, next to which in the 18th century the rural farmhouse was built which houses the small museum with the finds discovered in the Villa.